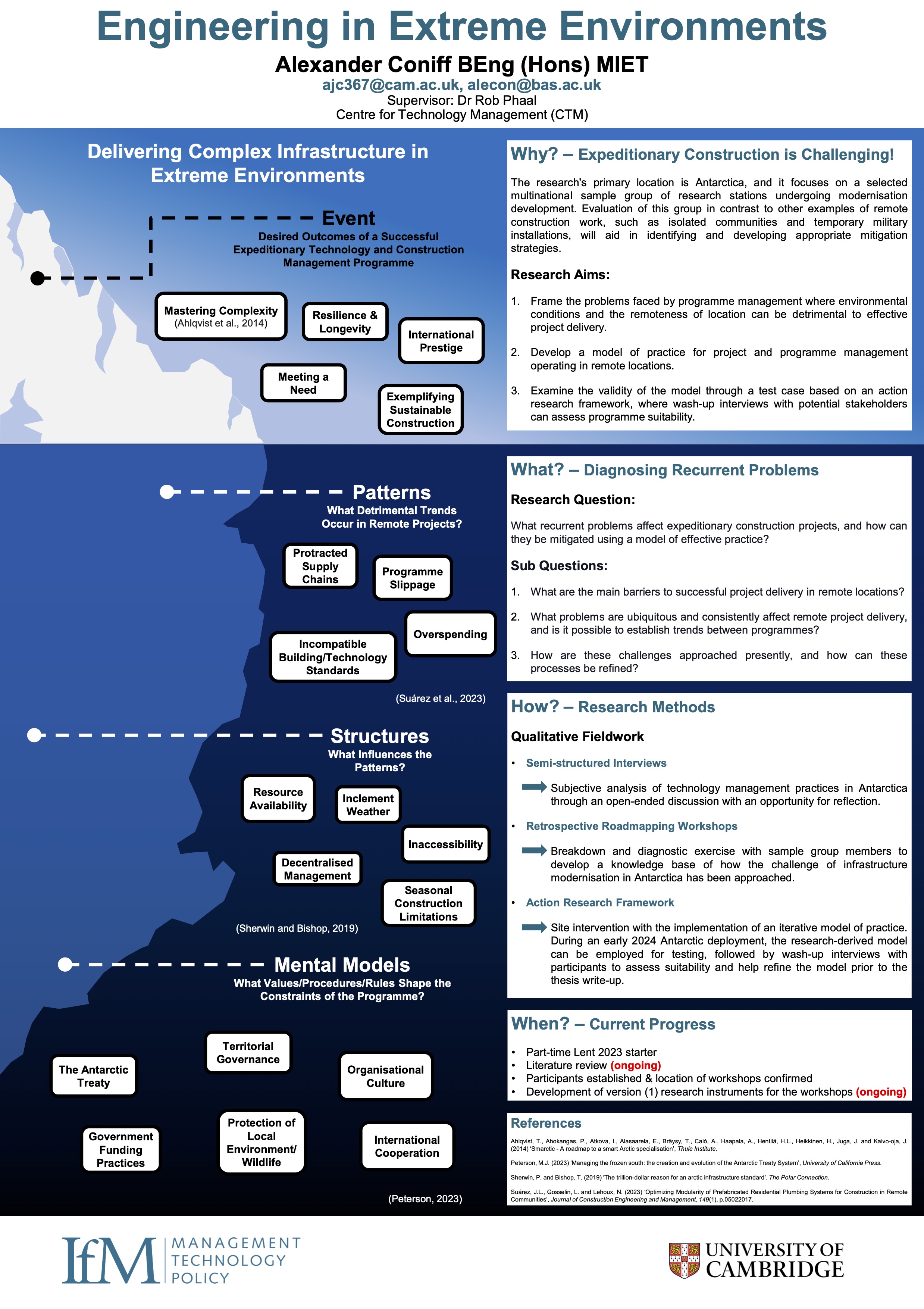
Engineering in Extreme Environments
Alex Coniff
Construction in remote locations is characteristically a challenging enterprise fraught with complexities that can detrimentally affect maintaining budget limitations and meeting planned timeframes. The causes can be multifaceted...
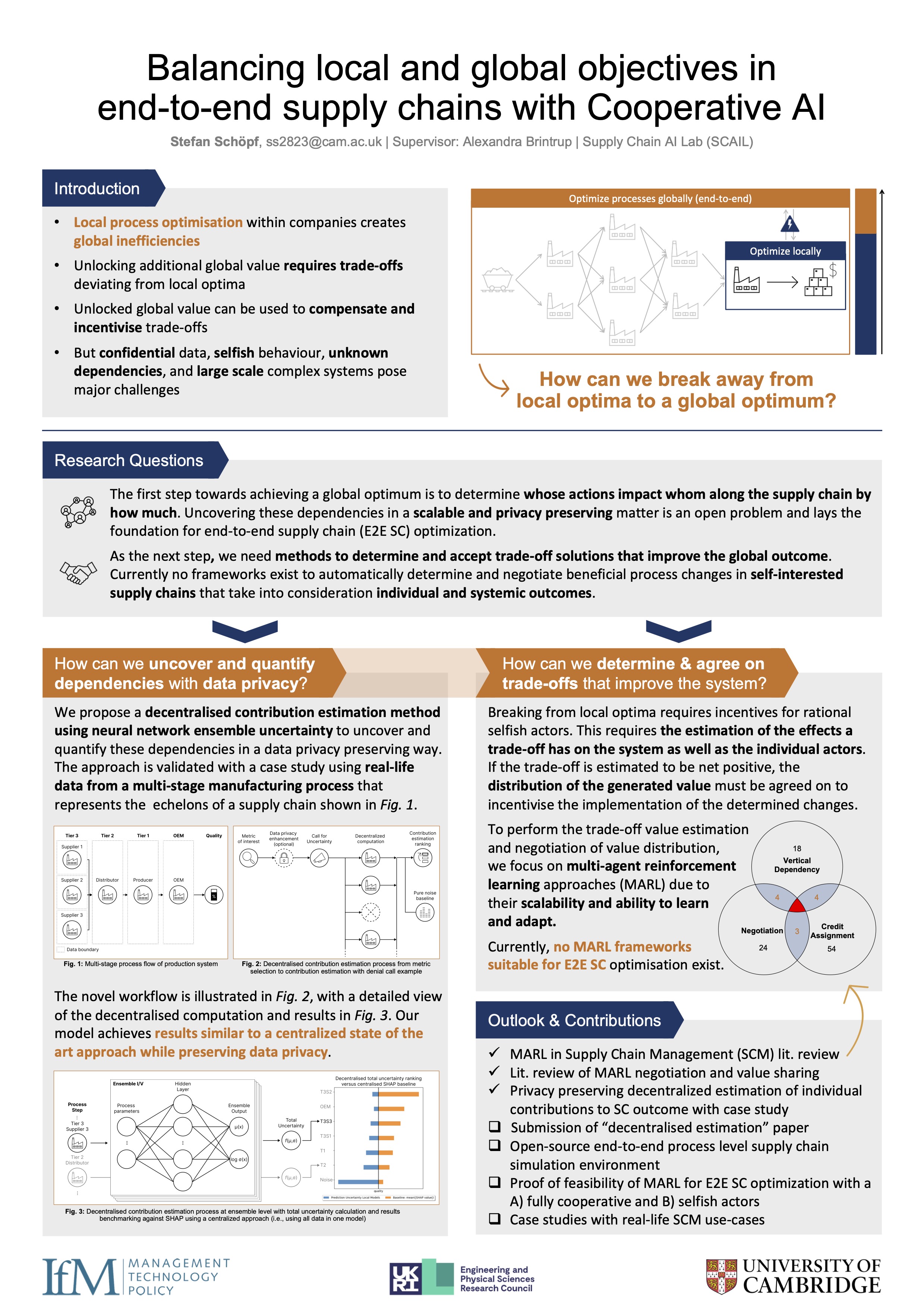
Balancing Local and Global Objectives in End-to-end Supply Chains with Cooperative AI
Stefan Schöpf
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is increasingly leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for tasks such as inventory management. While these AI applications have the potential to improve upon established operations research methods, a fundamental problem remains: Each company optimises their processes...
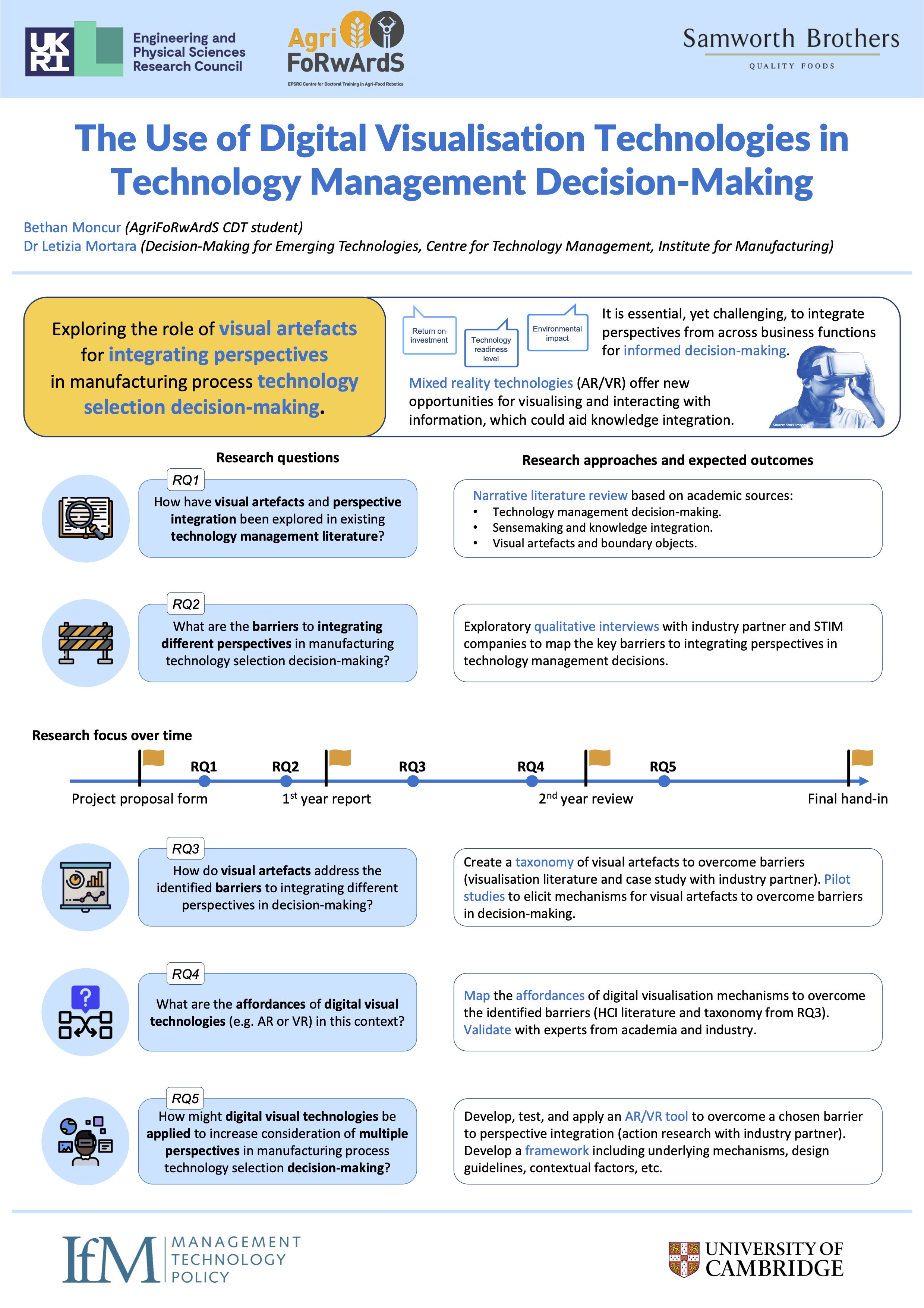
Integrating Multiple Perspectives in Technology Management Decisions
Bethan Moncur
Technology management decisions involve balancing technological considerations with wider business objectives in an operating environment that is complex, uncertain, and dynamic. This requires effective integration of information from multiple sources...
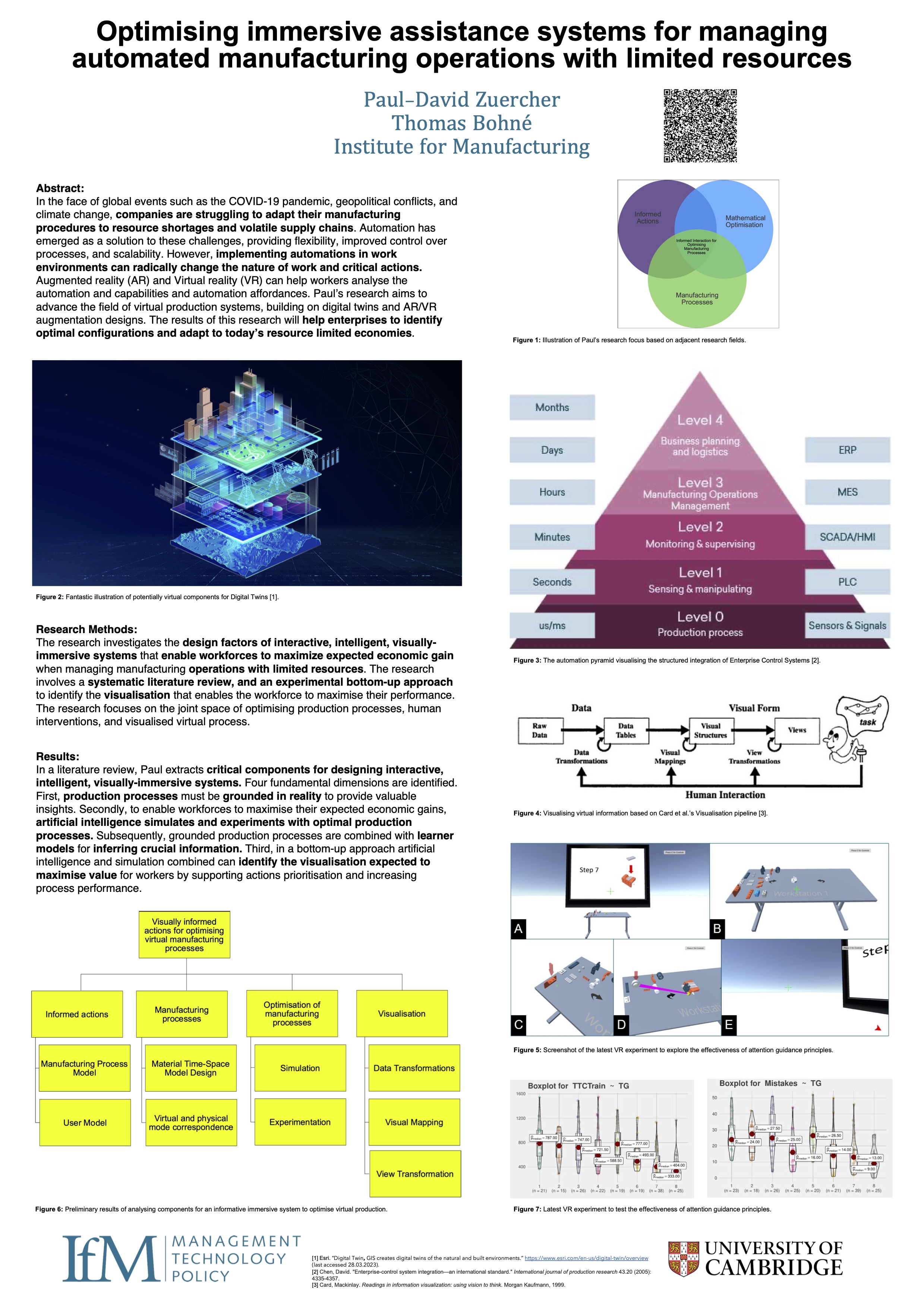
Optimising Immersive Assistance Systems for Managing Automated Manufacturing Operations with Limited Resources
Paul-David Zuercher
In the face of global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical conflicts, and climate change, companies are struggling to adapt their manufacturing procedures to resource shortages and volatile supply chains. Automation has emerged as a solution to these challenges...

Strategic Decisions During Patent Preparation and Prosecution Potentially Leading to Different Firm-Level Outcomes
Geoffrey White
On a firm-level, which decisions during patent preparation and prosecution lead to long-term favourable business outcomes, such as maximum revenue growth or greatest market share? Patent preparation involves interaction...

Application of Pose Estimation in Augmented Reality for Virtual Physical Rehabilitation
James Tombling
Markerless motion capture is a rapidly developing area within the fields of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Computer Vision (CV) with numerous applications in various industries, including entertainment, healthcare, and sports. In recent years...

Designing Food Supply Chain for Nutritional Delivery & Traceability
Garry Clawson
This PhD research focuses on developing and understanding relationships between supply chain design and product functionality within the context of food supply chain and nutrition. Since the green revolution food supply chain management has focused...

Ultra-fast Pulsed Laser Deposition (UF-PLD) of Thin Films for Application in Air-Breathing Electric Propulsion
Bensun Chun Pang Law
Air-breathing electric propulsion (ABEP) is an intriguing key technology that can be used to achieve very low Earth orbits for low latency communications or more comprehensive Earth observation. The term "air-breathing electric propulsion" refers...
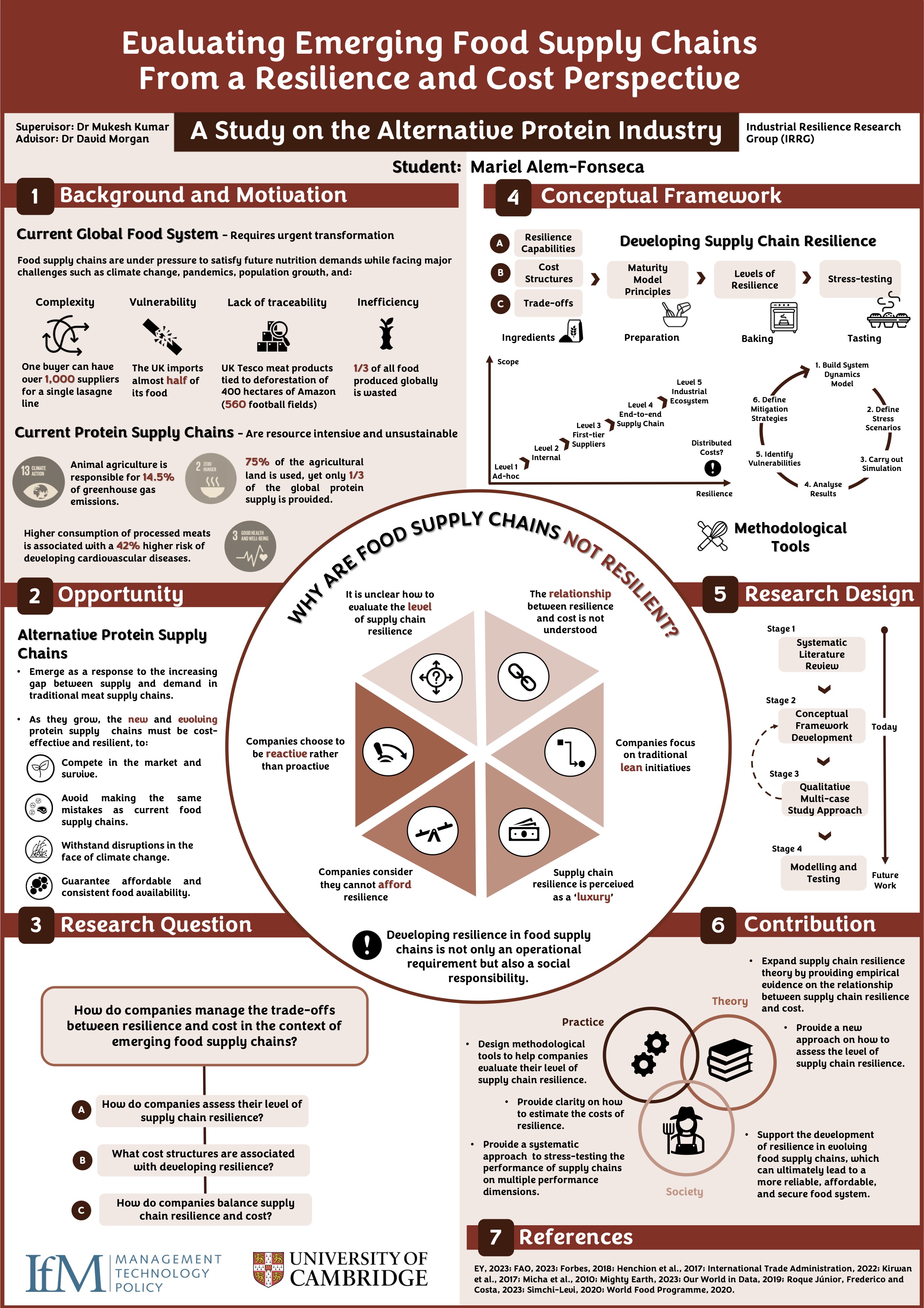
Evaluating Emerging Food Supply Chains from a Resilience and Cost Perspective: A Study on the Alternative Protein Industry
Mariel Alem Fonseca
This study aims to examine the relationship between resilience and cost across the dimension of sustainability (i.e., economic, environmental, societal) in alternative protein supply chains (SCs). Our global food system is on the cusp of transformation...
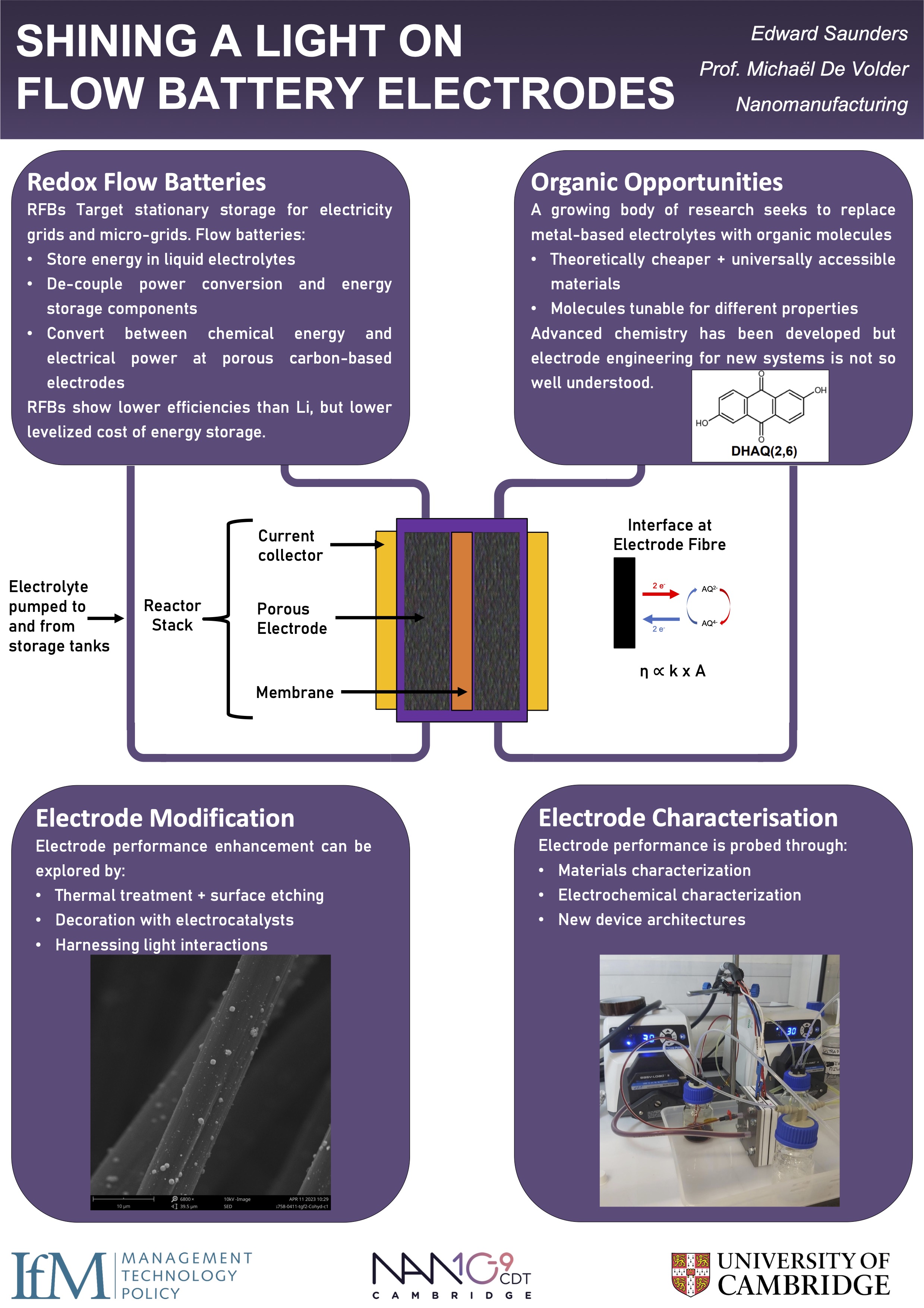
Shining a Light on Redox Flow Battery Electrodes
Edward Saunders
Having emerged as a cheap and renewable source of energy, the increasing use of solar and wind energy presents issues to electricity grids and other practical stationary deployments due to their intermittency. Thanks to their ability to store energy...
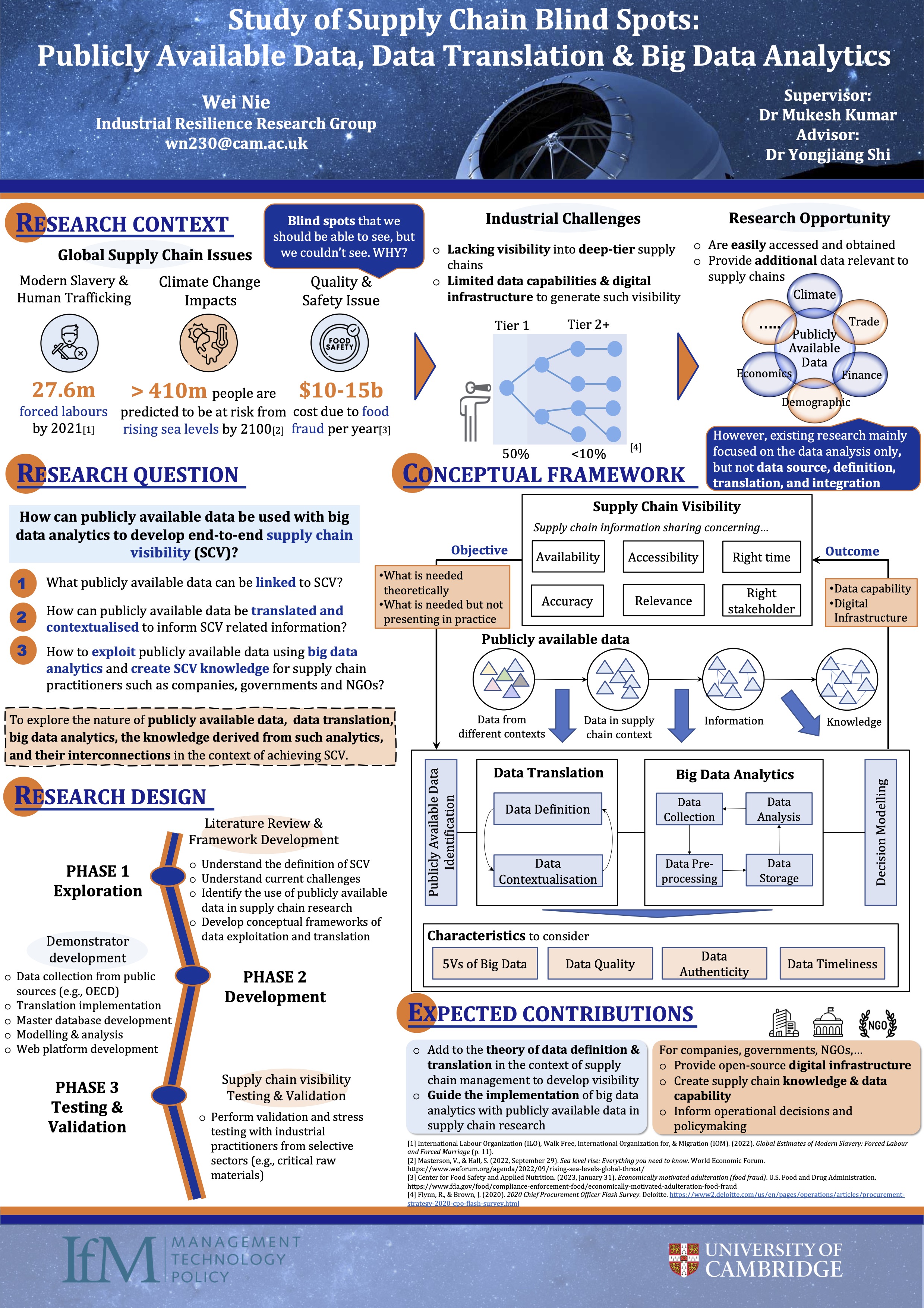
Study of Supply Chain Blind Spots: Publicly Available Data, Data Translation & Big Data Analytics
Wei Nie
This study explores the nature of publicly available data, data translation, big data analytics, the knowledge derived from such analytics, and their interconnections in the context of achieving supply chain visibility (SCV) to uncover the blind spots...
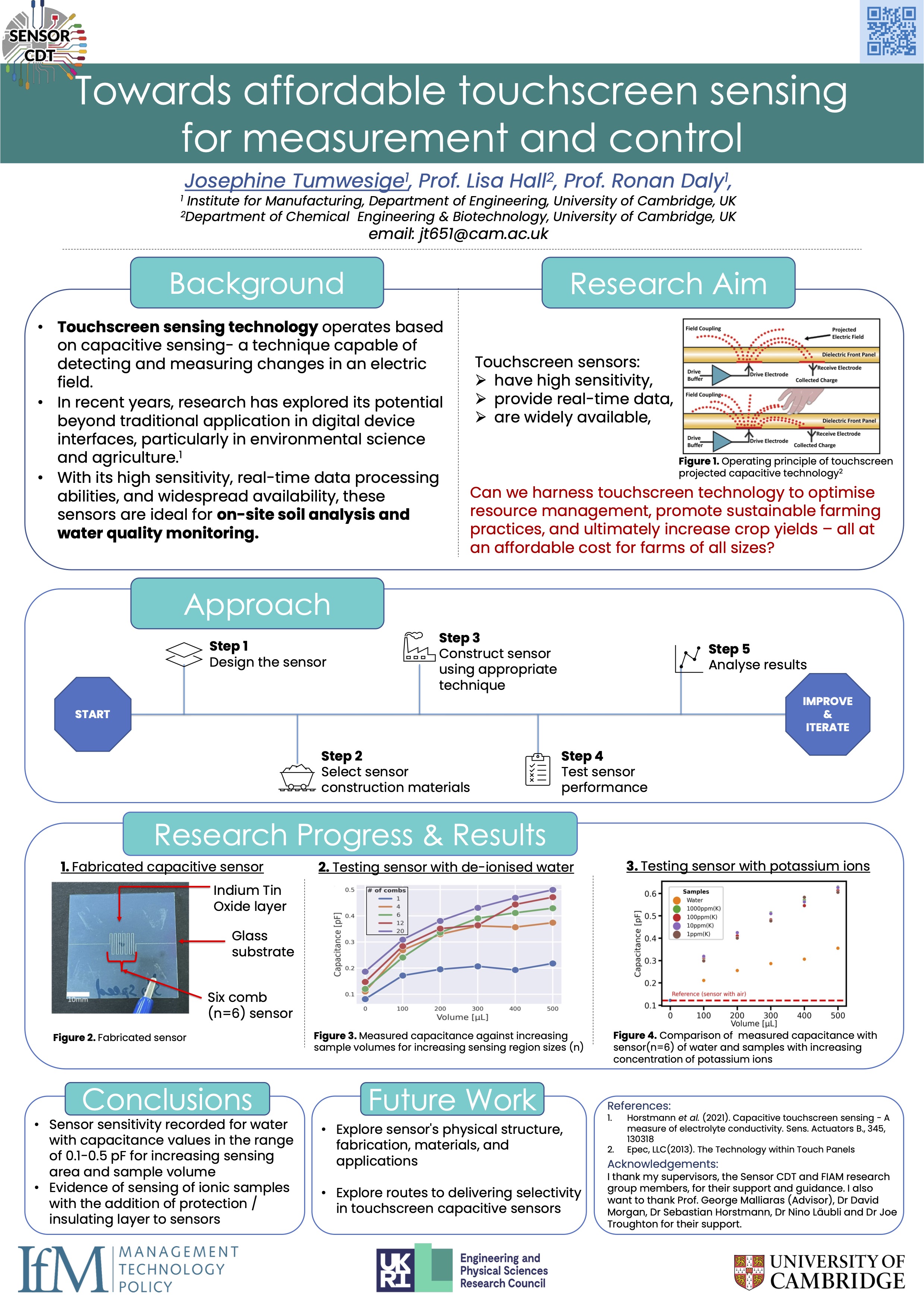
Towards Affordable Touchscreen Sensing – Linking Device Fabrication with Control of Fringe Field Interactions
Josephine Tumwesige
Touchscreen technology has become integral to our interactions with electronic devices, from smartphones and tablets to industrial control systems. Capacitive sensing, the predominant method for touchscreen sensing, relies on the principles of acapacitor. Acapacitor consists of...
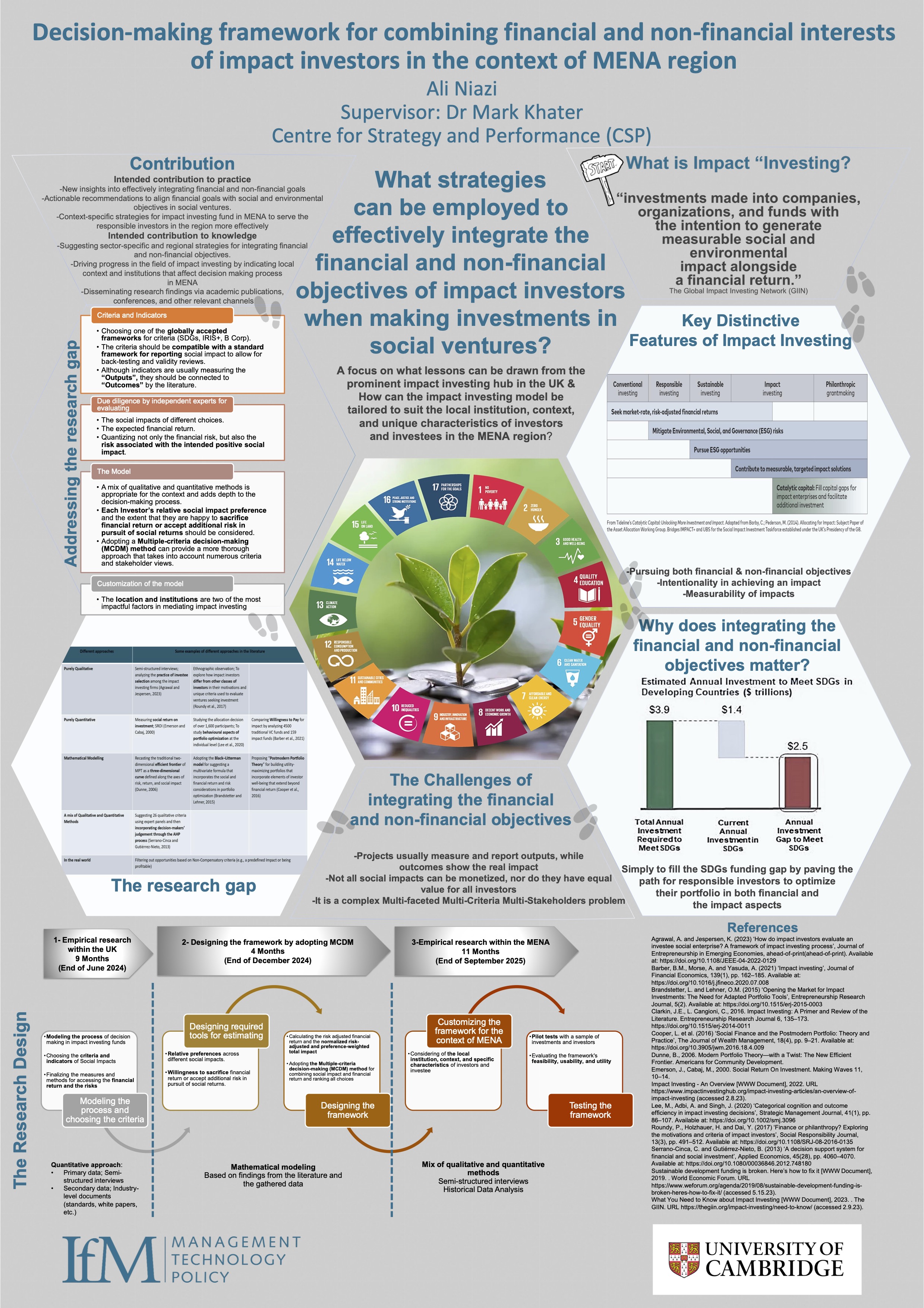
Decision-making Framework for Combining Financial and Non-financial Interests of Impact Investors in the Context of MENA
Ali Niazi
Social enterprises can contribute to addressing the world’s seemingly intractable problems. However, social enterprises, like traditional corporations, need capital to fuel their growth. Research suggests the lack of finance as one of the most significant barriers to the growth...

Cognitive Network-based Systems Approach - To Minimise Failures in Complex Industrial Systems
Hanu Priya Indiran
Social enterprises can contribute to addressing the world’s seemingly intractable problems. However, social enterprises, like traditional corporations, need capital to fuel their growth. Research suggests the lack of finance as one of the most significant barriers to the growth...

Decoding the Industry Ecosystems: Through Exploring the Evolution of Chinese Logistic Industry
Nan Sun
In terms of research concerns, the study aims to propose an innovative industrial ecosystem framework to synthesise and guide competition and cooperation among players from the perspective of supporting the healthy and sustainable developmenth...

Risk-aware Decision-Making Process of Hospital Facility Management
Momoko Nakaoka
Acute hospitals are one of the most complicated facilities involving multiple players and spaces in dynamically evolving social and environmental context. Hospital Facility Management(HFM) covers a wide range of activities, such as maintenance of equipment, timely closure of non-clinical requests...
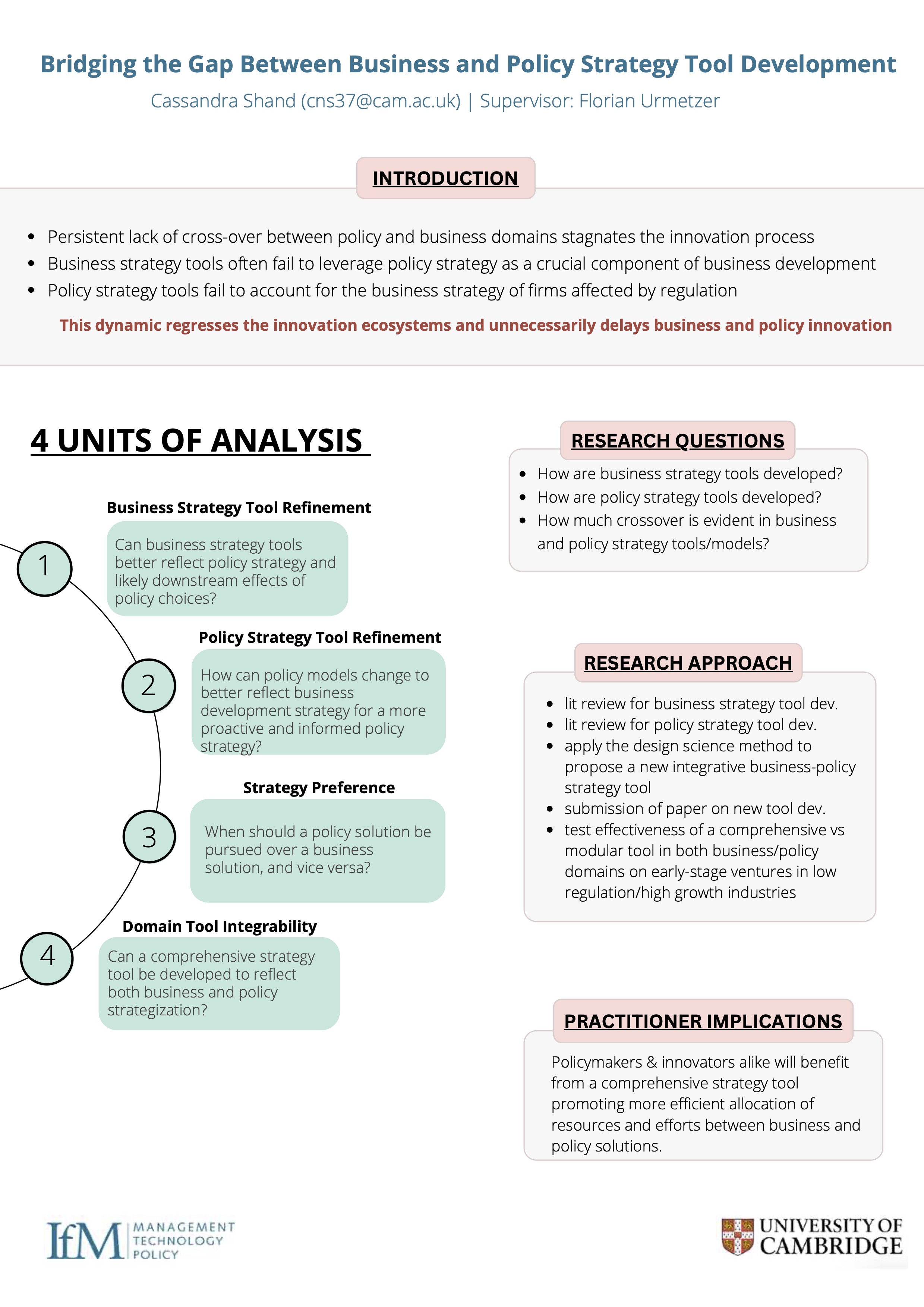
Bridging the Gap Between Business and Policy Strategy Tool Development: Towards a Comprehensive and Collaborative Framework
Cassandra Shand
The development of business and public policy strategies are frequently considered separate and distinct processes, with existing development models often underestimating the potential impact of one domain on the other. However, as rapid innovation advances, the persistent lack of crossover...

Smart Sensing Method for Low-cost & Green Data Collection
Luning Li
IoT is a ubiquitous technology. It connects every physical object and enables relatively low-cost and large-scale data gathering from large volumes of sensors. Once a small piece of data is captured by a sensor, it will follow the IoT network and enters the vast IoT value chain to become value-added...
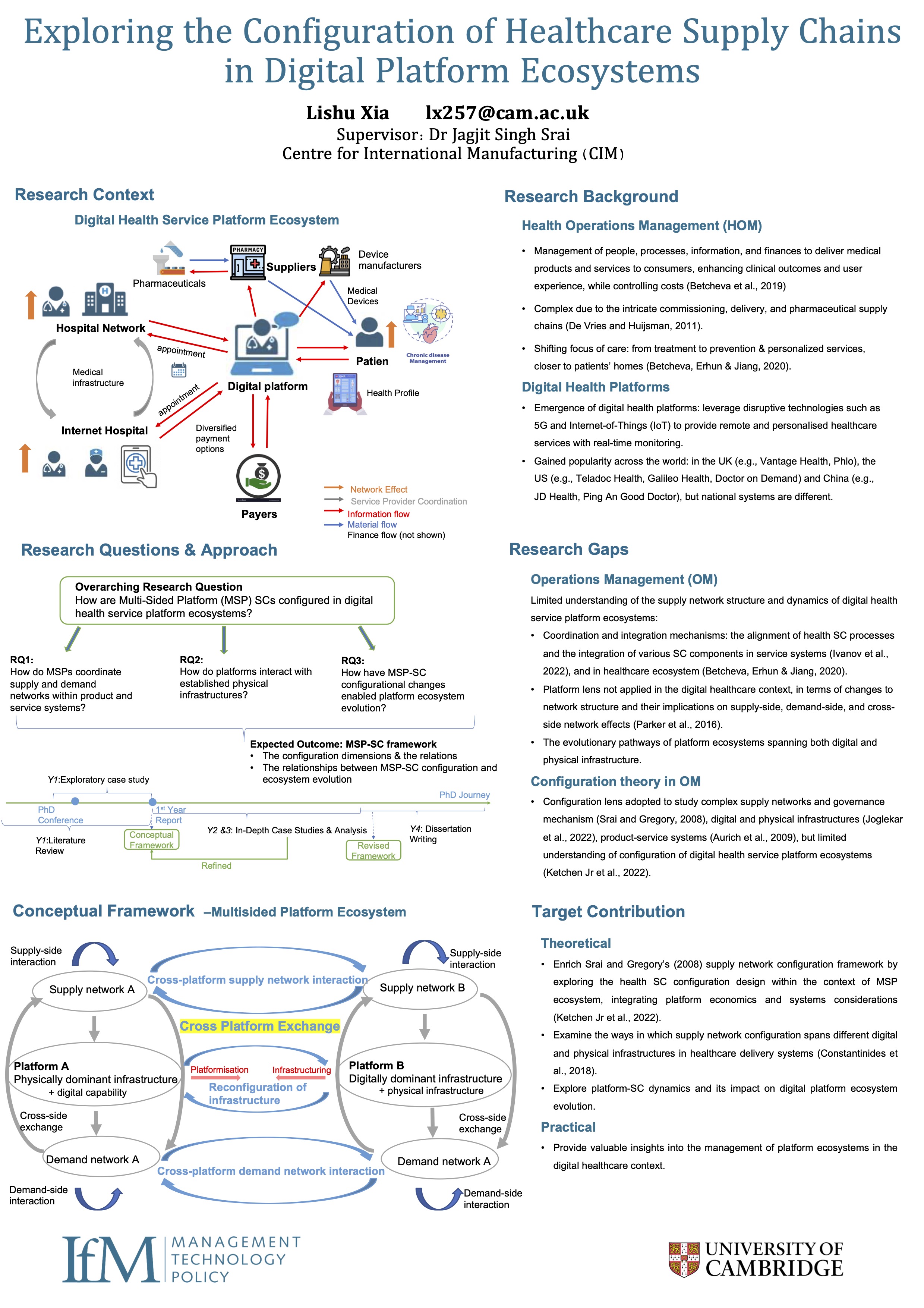
Exploring the Configuration of Healthcare Supply Chains in Digital Platform Ecosystems
Lishu Xia
IoT is a ubiquitous technology. It connects every physical object and enables relatively low-cost and large-scale data gathering from large volumes of sensors. Once a small piece of data is captured by a sensor, it will follow the IoT network and enters the vast IoT value chain to become value-added...

Scaling Quality Assurance in Additive Manufacturing via Transfer Learning
Christos Margadji
Additive manufacturing enables the production of extremely complex parts but suffers from frequent failure modes, limiting its potential in risk-averse applications. Recent developments have demonstrated how an AI can be deployed...

Strategy and Project Portfolio Management in Capital- intensive Mining Firms
Killian Manyuchi
Capital allocation is critical for mining and metals businesses. Because of their finite and depleting nature, they require continuous reinvestment to yield justifiable returns. The most attractive ‘assets’ should form the core of the business, and the least attractive...

Incoherence of Business Model Innovation in Digital Transformation
Chen Ye
Firms face various challenges inbusiness model innovation (BMI) in digital transformation (DT). To study this problem, the coherence view of internal fit has been extensively studied in strategy and business models. In addition, a dialectical alternative to fit-based models of strategy emphasizes...